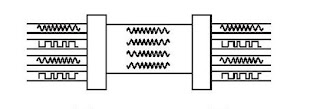
Figure illustrates frequency-division multiplexing (FDM). This technique works by converting all data channels to analog form. Each analog signal can be modulated by a separate frequency (called a "carrier frequency") that makes it possible to recover that signal during the demultiplexing process. At the receiving end, the demultiplexer can select the desired carrier signal and use it to extract the data signal for that channel. FDM can be used in broadband LANs. (A standard for Ethernet also exists.) One advantage of FDM is that it supports bidirectional signaling on the same cable. That is, a frequency can originate from both ends of the transmission media at once.
No comments:
Post a Comment